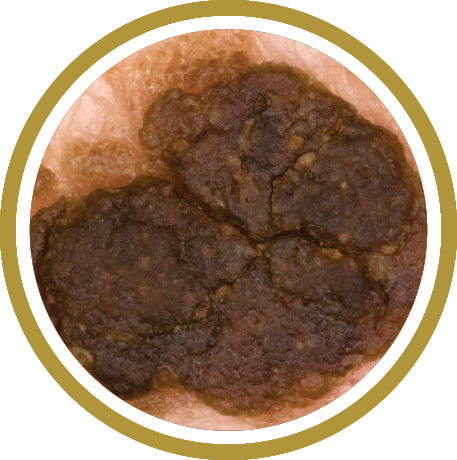
Malignant Melanoma
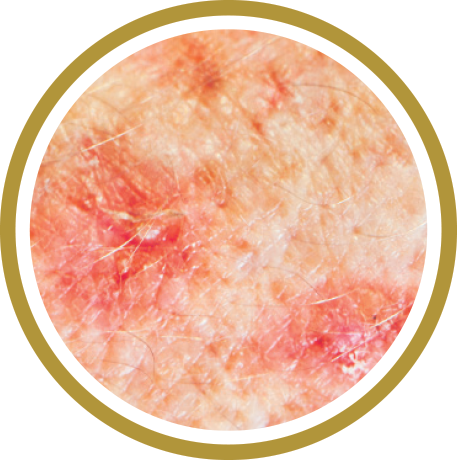
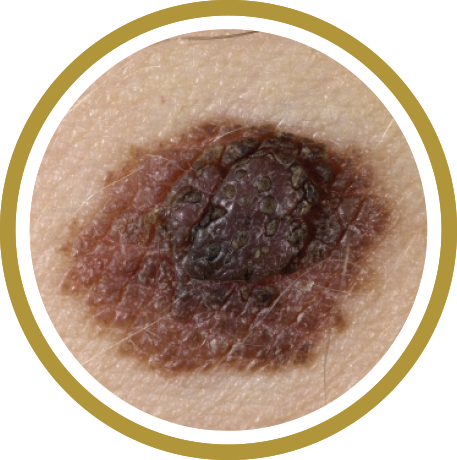
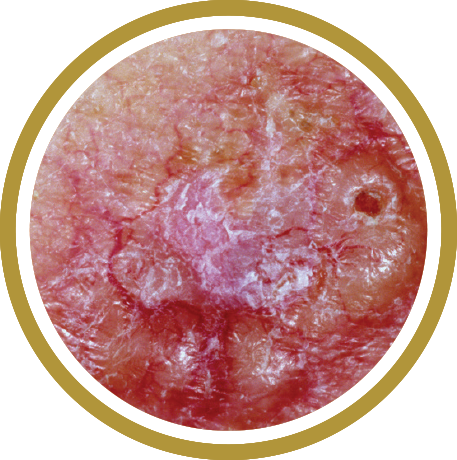
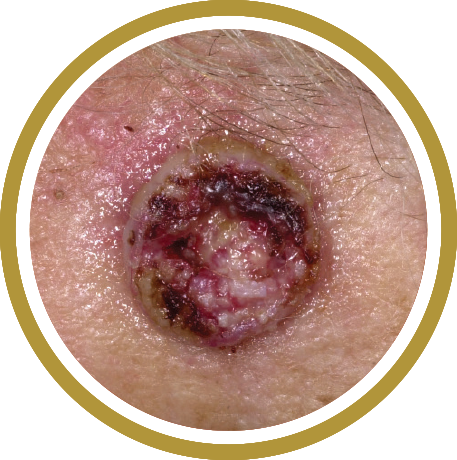
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer of the cells that produce the dark, protective pigment in your skin (melanin). Melanoma may affect anyone at any age.Appearance
Melanoma can occur anywhere on the body. People with dark complexions can also develop melanoma, especially on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, under nails, and in the mouth.Individual lesions may appear as a dark brown, black, or multicolored growth with irregular borders that can become crusted and bleed. Check for spots that meet one or more of the ABCDE guidelines of melanoma. Those are:
- Asymmetry
- Border irregularity
- Color variability
- Diameter of 6mm or more
- Evolution or change in appearance or an appearance different from other moles
Learn how to examine your skin
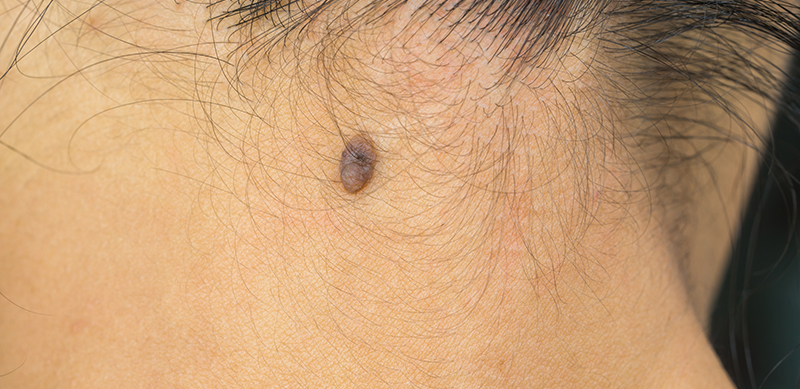
Risk factors of malignant melanoma
Overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering, is a major cause of melanoma. People who have fair skin, light hair and eye color, a family history of melanoma, or who have had melanoma in the past have an increased risk of developing this disease.Melanoma can arise in or near a preexisting mole, or may appear without warning. It may spread to other organs, making it essential to treat this skin cancer early.